From `File|New Project` to Azure: A brief overview of the new .NET Aspire
.NET Aspire is an opinionated, cloud ready stack for building observable, production ready, distributed applications. So what exactly does this mean? What problems does it solve? How it can help me deploy distributed applications to Azure?
Let’s quickly go over these questions…
What is .NET Aspire
.NET Aspire (currently on preview 2 ) is a powerful tool for developing and deploying cloud-native applications on containers, simplifying many common challenges associated with orchestration, service connectivity, and monitoring. Some of the key features .NET Aspire offers are:
-
Cloud-Native Development: .NET Aspire enables the development of cloud-native applications, which are designed to leverage the scalability, flexibility, and resilience of cloud environments.
-
Containerization: It helps with containerization of the applications and supports running applications within containers, allowing for consistent deployment across different environments.
-
Orchestration: .NET Aspire assists with orchestration tasks, such as service discovery, managing environment variables, and configuring containers. This helps abstract away low-level implementation details, streamlining the development process.
-
Connectivity to Services: The platform simplifies connecting applications to popular services like databases, Redis, Azure Service Bus, and others, by providing pre-built components to facilitate integration.
-
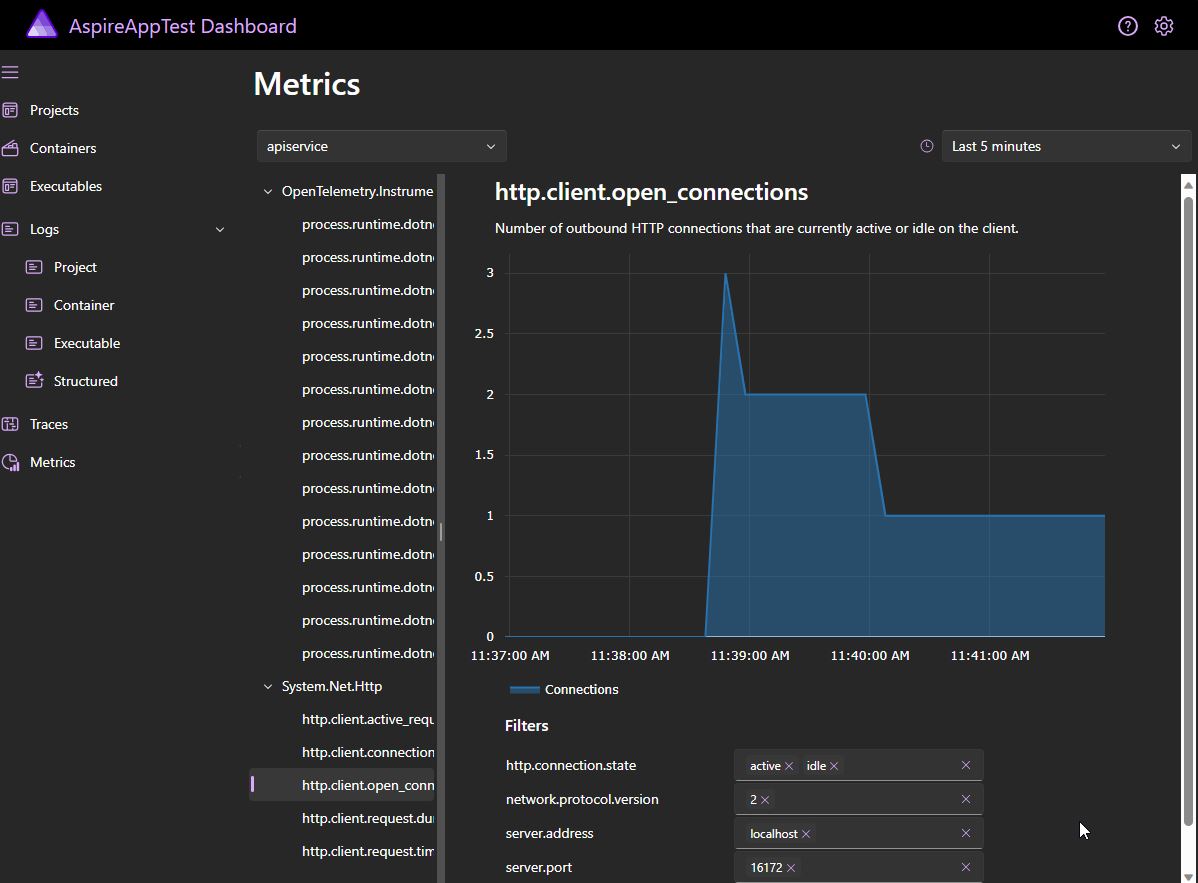
Monitoring and Inspection: .NET Aspire includes a sophisticated dashboard for comprehensive application monitoring and inspection. This feature provides visibility into application performance, resource usage, and other metrics, aiding to help the developer in troubleshooting and optimization.
Overall, .NET Aspire appears to offer a comprehensive solution for building, deploying, and managing modern cloud-native applications, with features geared towards enhancing developer productivity and operational efficiency.
.NET Aspire in relation to other known Microsoft Frameworks
Reading overview of .NET Aspire may ring a bell or two. It might remind you of Microsoft Orleans or dapr. Are they similar, substitutes or complementary frameworks?
- Orleans is a cross-platform actor-based framework for building robust, scalable distributed applications. An Orleans-based solution will still have external dependencies such as data stores and caches for which .NET Aspire can be used for orchestration purposes. Support for Orleans will be added in .NET Aspire soon.
- Dapr and .NET Aspire are definitely complementary technologies. NET Aspire provides opinionated configuration around the underlying cloud technologies without abstracting them, whereas Dapr hides some cloud platform details. A .NET dapr enabled application can utilize NET Aspire to make the developers’ everyday tasks easier and help them deploy to Azure more smoothly.
.NET Aspire - File|New Project experience
In the time of writing, the prerequisites for creating a .NET Aspire project and easily deploy it to Azure, among others are:
- .NET 8.0
- Visual Studio 2022 Preview (Version > 17.9)
- Docker Desktop
- Azure Developer CLI
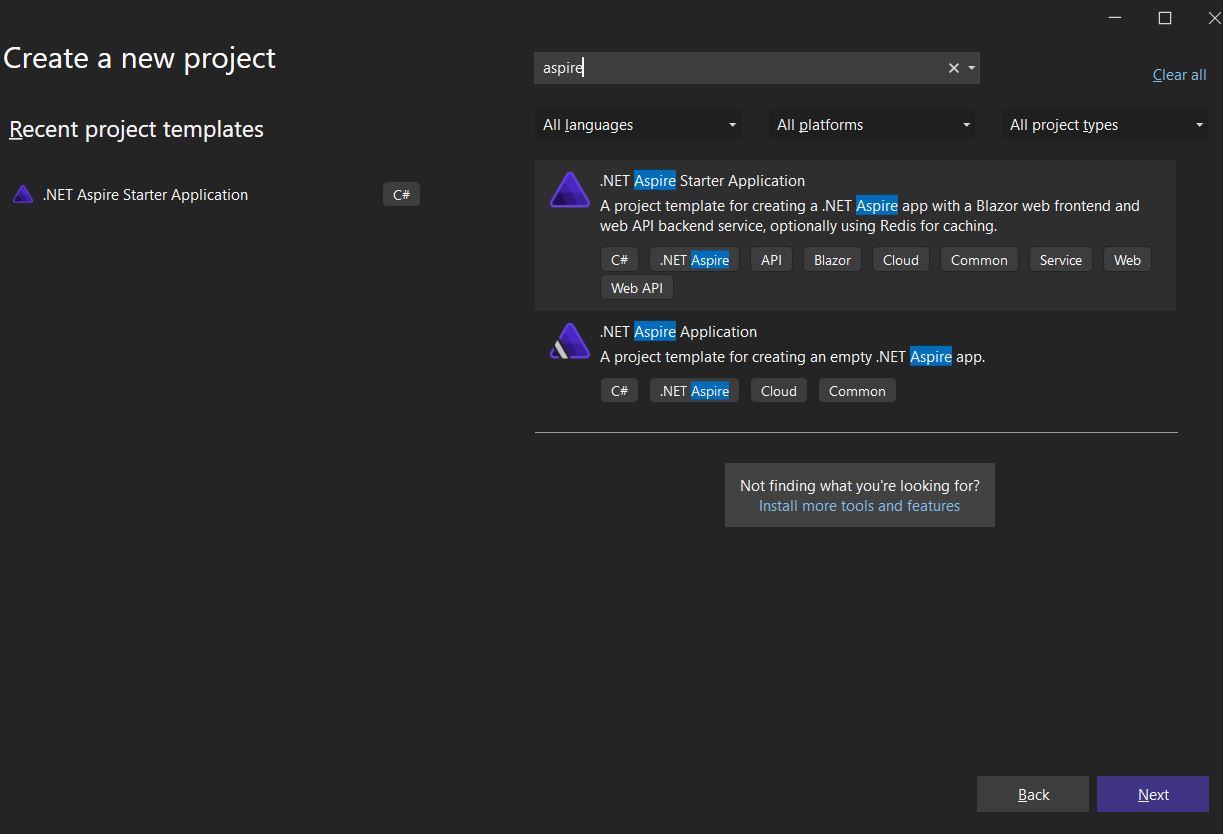
The easiest way to explore a .NET Aspire application is to use the Visual Studio application template. Open your Visual Studio 2022 Preview, select “Create a new project”, search for aspire and select the .NET Aspire Starter Application as shown below:
Alternatively, you can fork and use this, slightly more sophisticated, sample app for your tests.
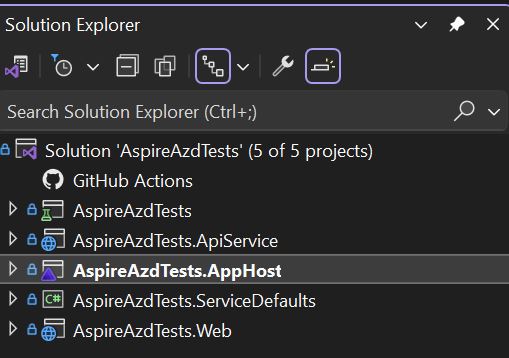
The default solution consists of the two actual projects that you would expect for a web based visual studio solution:
- XXX.Web: The the web-front project (.NET Core Blazor App project)
- XXX.ApiService: ASP.NET Core Minimal API project is used to provide data to the front end (XXX.Web)
Apart from those two projects, the solutions contains two more projects, that make up the Aspire aspect of your solution
- XXX.AppHost: The Orchestrator project designed to connect and configure the different projects and services of your app, this is set as the the startup project of your solution
- XXX.ServiceDefaults: .NET Aspire shared project to manage configurations that are reused across the projects in your solution related to resilience, service discovery, and telemetry.
Deployment of .NET Aspire app to Azure
.NET Aspire apps are designed be containerized. The out-of-the-box deployment experience (at the time of writing) is to deploy your .NET Aspire app on Azure Container Apps with the help of Azure Developer CLI. Azure Container Apps is a fully managed serverless platform that allows you to maintain less infrastructure and save costs while running microservices and containerized applications.
Deploy everything to Azure Container Apps
The (really easy) way to deploy your app to Azure Container Apps is described in full detail in the documents below
- Deploy a .NET Aspire app to Azure Container Apps
- Deploy a .NET Aspire app to Azure Container Apps using the Azure Developer CLI (in-depth guide)
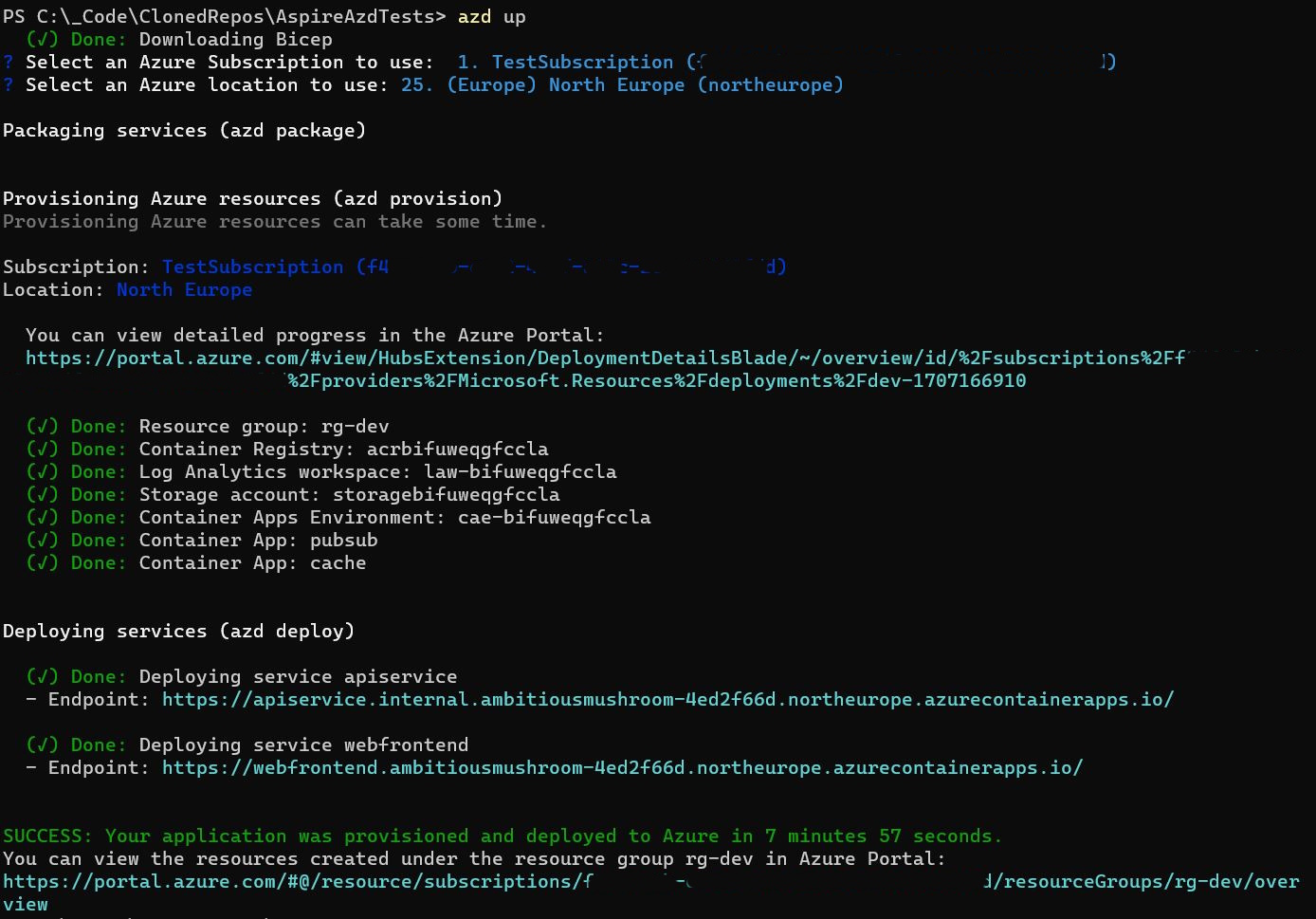
All you need to do is to run just two commands:
azd initazd up
This is all you need! Just that. The first command will initialize the template - it will inspect the local directory structure and determine that this is a .NET Aspire App
Azd up command under the hood will provision your infrastructure and deploy to Azure in one step. Alternatively, you can run azd provision then azd deploy to accomplish the tasks separately. The resource provisioning is done auto-magically but you can also modify how the infrastructure is created.
For instance you might need to change the name of the resource group that it will be created (by default it will give it the name rg-<environment-name>, ie rg-test). To do that run azd infra synth to persist it to disk. In that case, some additional directories and files will be created, as below:
1
2
3
- infra/ # Infrastructure as Code (bicep) files
- main.bicep # main deployment module
- resources.bicep # resources shared across your application's services
Deploy .NET Aspire to AKS
AZD CLI magic works (currently) just for the Azure Container Apps. If you wish to deploy your app to another container platform, like Azure Kubernetes Service, you need to use the community-developed tool Aspire8 for deploying .NET Aspire apps to Kubernetes. This tool leverages the Aspire manifest to automate deploying Aspire apps to Kubernetes clusters. The steps to do the deployment of the .NET Aspire app to Kubernetes cluster are the following
- Before you start, you need to have the necessary infrastructure already deployed, i.e. the AKS Cluster, the Azure Container Registry etc.
- Install the Aspirate tool as a global tool in your development machine
1
2
3
4
5
# Installing as a Global Tool
dotnet tool install -g aspirate --prerelease
# or update if an older version is already installed
# dotnet tool update -g aspirate --prerelease
- Login to the ACR so that the container images can be pushed there
1
az acr login --name acrttxxxx.azurecr.io
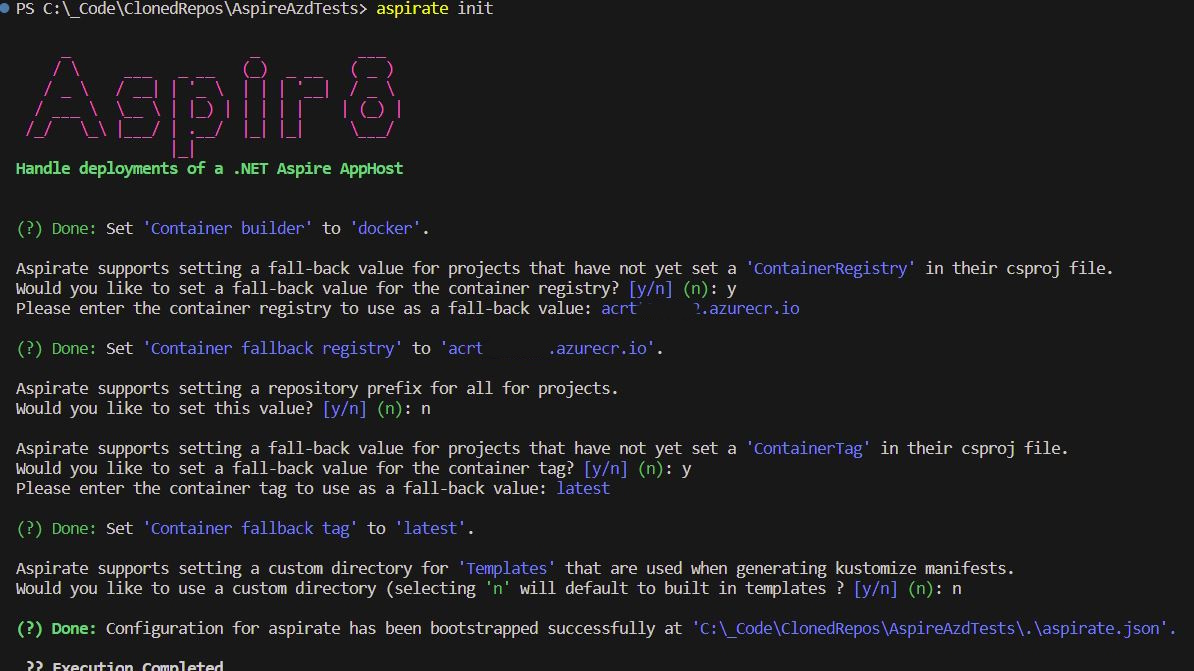
- Initialize the aspirate tool, by bootstrapping certain settings such as Container Registry that will be used for your container builds.
1
aspirate init
- Building Projects and Containers The Build command will build all projects defined in the aspire manifest file, and push the containers to the registry (if specified), or the local docker daemon
1
aspirate build --container-registry acrttxxx.azurecr.io
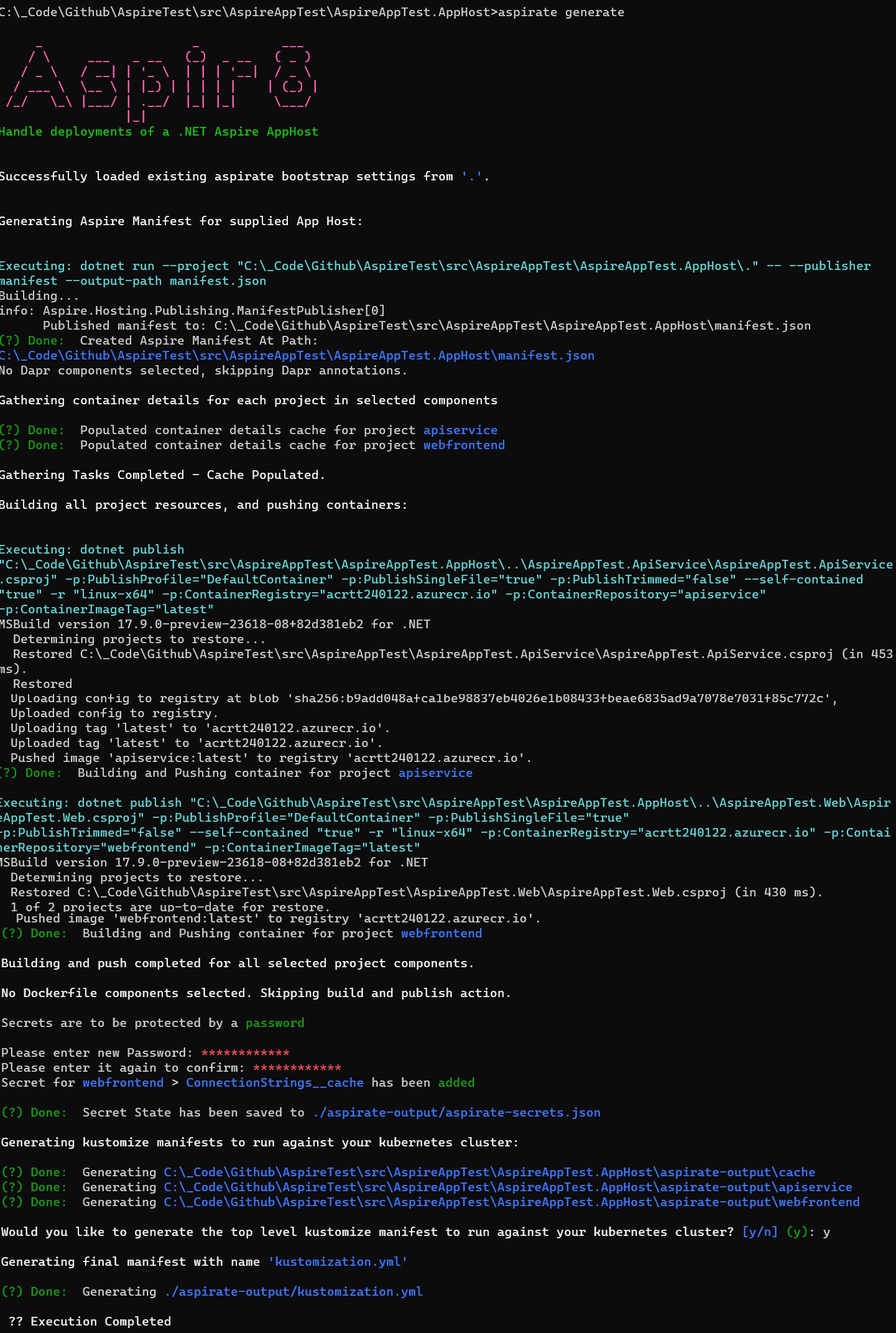
- Generate Manifests and Secrets
The Build command will build all projects defined in the aspire manifest file, and it will generate all the necessary
kustomizefiles.
1
aspirate generate
- Apply Manifests to a Cluster
Running the
applycommand will prompt you for information (i.e. if you want to connect in the k8s context in your kubeconfig file) and if you have a secret file, you will be prompted to enter the password to decrypt it.
1
aspirate apply
Final Thoughts
.NET Aspire seems like a rather compelling solution for building and deploying modern, cloud-native applications with ease. By streamlining the development process and abstracting away low-level implementation details, it empowers developers to focus on building robust, scalable cloud-native applications.
Whether you’re a seasoned developer or just starting out, .NET Aspire offers a user-friendly experience and comprehensive toolset to meet the demands of today’s cloud-native landscape. With its opinionated approach .NET Aspire equips developers with the tools they need to succeed in building and deploying production-ready cloud-native applications.